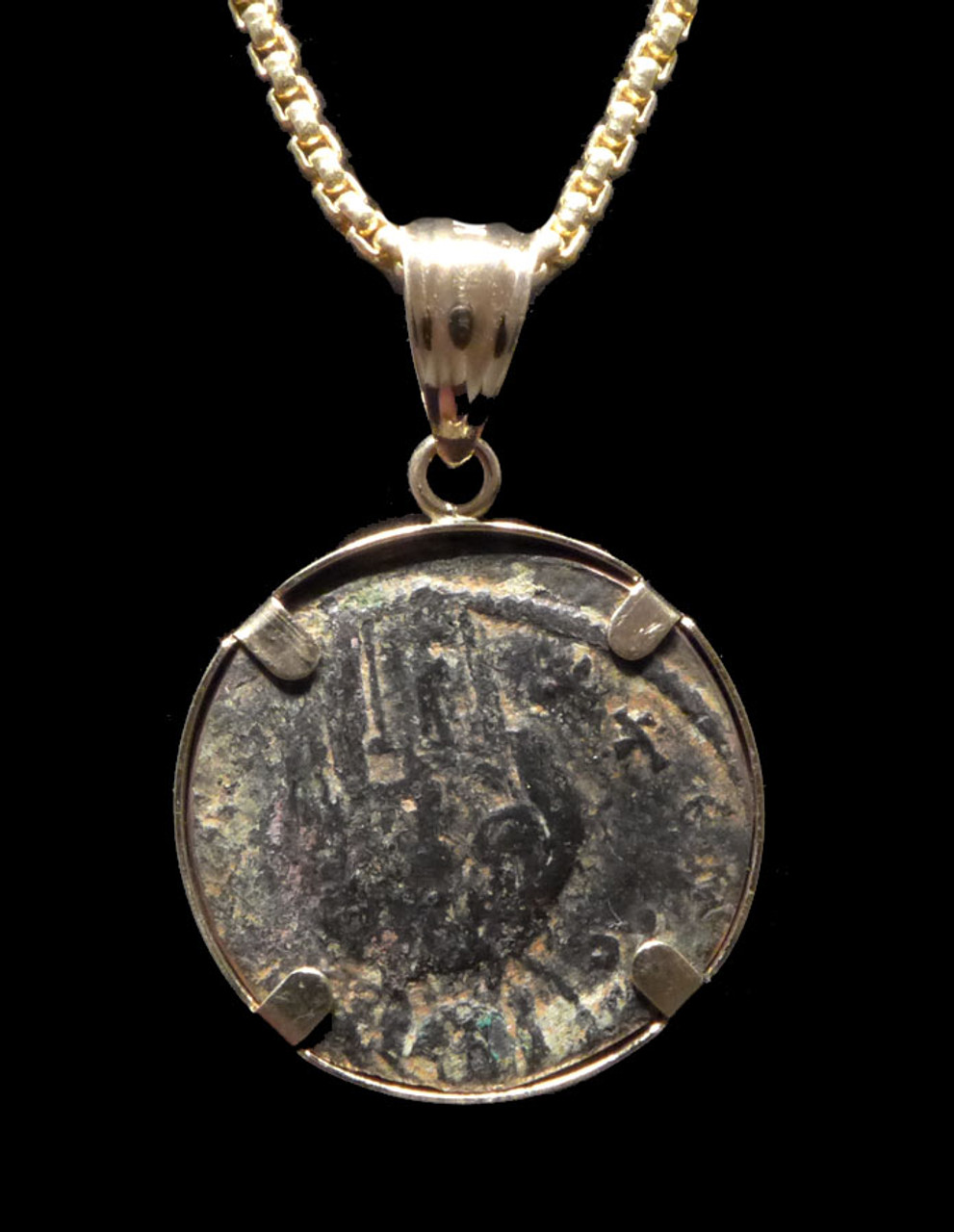
Product Description
This stunning ancient bronze Roman Byzantine follis coin is set in a 14KY gold which perfectly compliments the rich chocolate brown patina. This coin is called an anonymous bronze follis because the ruling emperor was not depicted on the obverse but instead, Christ. It has been mounted to display the reverse side showing a bold inscription in Greek (the common language of the day of Byzantine Roman Empire), "IC - XC / NI-KA" which translates to "Jesus Christ Conquers". The back side shows Jesus with halo, holding a Bible. The image is upside down because that is all these coins were struck opposite to the other side but, if you are wearing this pendant and flip the coin to see the back side, this image of Christ would be right side up to the wearer's viewpoint. An impressive antiquity of ancient Christianity and highly recommended. This coin was minted under the rule of Michael IV and dates from 1034 A.D. to 1041 A.D..
As a modern representative of one's Christian beliefs, wearing a pendant featuring one of these genuine ancient Christian Roman coins is a far more unique display of one's faith compared to a modern made, mass-produced cross on a chain.
*** Chain is not included but may be purchased additionally, at the link below
GUARANTEE: ALL PURCHASES ACCOMPANIED WITH A WRITTEN GUARANTEE OF AUTHENTICITY
SETTING: 14KT YELLOW GOLD
COIN: BRONZE FOLLIS
COIN AGE: 1034 - 1041 A.D.
DIMENSIONS: .8" or 23 mm overall diameter
:::: Includes Gift Box
:::: Includes CERTIFICATE OF AUTHENTICITY / HISTORY SHEET
ADD THE DISPLAYED MEDIUM ROUND BOX 14K GOLD CHAIN
SEE MORE ANCIENT BYZANTINE ROMAN COIN JEWELRY
HISTORY
The anonymous bronze follis series was a revolutionary design in Byzantine coinage. For countless centuries even dating back to the early Roman Empire, coins always featured an emperor and promoted the emperor's rule. As Christianity dominated the Roman Byzantine Empire, a break from tradition was instituted in their coin follis issues to purposely promote Christ and not a man, not even the emperor himself during his own rule. This was in keeping with Christian beliefs that man is insignificant in the light of God and no man should be worshipped but God alone. These coins typically feature an image of Christ looking straight at you on the obverse side with the reverse boldly written in Greek, "In Christ, Victory" or "Jesus Christ, King of Kings".
As a result of the Byzantine coinage reform carried out at the end of the fifth century AD, a whole new range of denominations was brought into being each clearly marked with it’s value as a multiple of the basic ‘nummus’. The Christian religion that permeated the Byzantine culture influenced decisions to use Greek numerals for the new coins as Greek was the language of the New Testament. The largest denomination, the FOLLIS, bore the mark of value “M” (40 nummi), the HALF FOLLIS “K” (20 nummi), the DECANUMIUM “I” (10 nummi), and the PENTANUMIUM “E” (5 nummi), introduced at a later period. Over time, imagery used on the Byzantine coinage became increasingly religious. A portrait of Christ first appears on coinage of Justinian II (685-695 AD). Religious images were later banned in 815 AD during the Iconoclastic Period but restored in 843 AD under the empress Theodora.
 US Dollars
US Dollars
 AUD
AUD
 CAD
CAD
 POUNDS STERLING
POUNDS STERLING
















